Introduction
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, has revolutionized various industries by enabling the creation of complex objects with ease. This technology has the potential to transform the way we produce and consume goods, making it a key player in the transition towards a circular economy. In this article, we will explore how 3D printing can contribute to closing the loop in the circular economy.
What is the Circular Economy?
The circular economy is an economic model that aims to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency. It is based on the principles of designing out waste and pollution, keeping products and materials in use, and regenerating natural systems. Unlike the traditional linear economy, which follows a “”take-make-dispose”” approach, the circular economy focuses on creating a closed-loop system where resources are continuously reused and recycled.
Benefits of 3D Printing in the Circular Economy
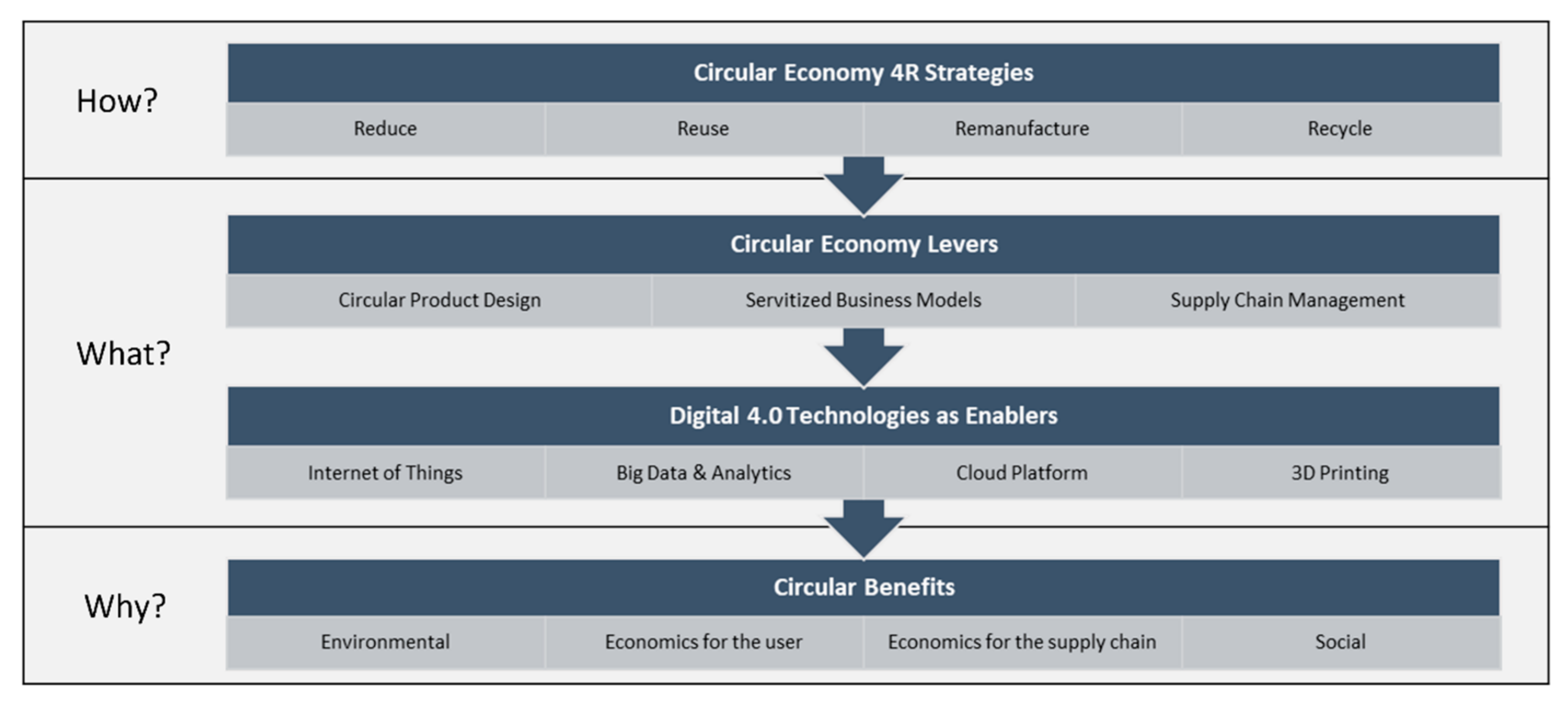
3D printing offers several advantages that align with the principles of the circular economy:
Waste Reduction
Traditional manufacturing processes often generate significant amounts of waste due to subtractive manufacturing techniques. In contrast, 3D printing is an additive process that only uses the necessary amount of material, minimizing waste generation. This reduction in waste aligns with the circular economy’s goal of eliminating waste and pollution.
Localized Production
3D printing enables localized production, allowing goods to be manufactured closer to the point of consumption. This reduces the need for long-distance transportation, which contributes to carbon emissions and resource depletion. By producing goods locally, 3D printing supports the circular economy’s aim of reducing the environmental impact associated with transportation.
Customization and Personalization
One of the key advantages of 3D printing is its ability to create highly customized and personalized products. This customization reduces the likelihood of products becoming obsolete or unwanted, extending their lifespan. By enabling personalized production, 3D printing promotes the circular economy’s principle of keeping products and materials in use for as long as possible.
Summary
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, allows for the creation of three-dimensional objects by layering materials based on a digital design. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, which often involve subtractive processes and generate significant waste, 3D printing offers a more sustainable alternative. By using only the necessary amount of material and minimizing waste, this technology aligns perfectly with the principles of the circular economy.
The circular economy aims to eliminate the concept of waste by designing products that can be reused, repaired, or recycled at the end of their lifecycle. 3D printing plays a crucial role in achieving this goal by enabling the production of customized and on-demand products, reducing the need for mass production and excessive inventory. This not only reduces waste but also minimizes transportation and storage costs, making the manufacturing process more efficient and environmentally friendly.
Furthermore, 3D printing allows for the use of recycled materials as feedstock, closing the loop even further. By converting waste materials, such as plastic bottles or discarded electronics, into printable filaments, 3D printers can create new products without the need for virgin resources. This not only reduces the demand for raw materials but also helps in tackling the growing problem of plastic pollution.
In conclusion, 3D printing technology has the potential to revolutionize the manufacturing industry and contribute significantly to the circular economy. By minimizing waste, enabling customization, and utilizing recycled materials, this innovative technology can help in closing the loop and promoting a more sustainable future. Embracing 3D printing in various sectors can lead to a significant reduction i top article n resource consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and environmental impact, making it a crucial tool in the transition towards a circular economy.
- Q: What is 3D printing?
- A: 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process of creating three-dimensional objects by layering materials based on a digital design.
- Q: How does 3D printing contribute to the circular economy?
- A: 3D printing enables the production of objects on-demand, reducing the need for mass production and minimizing waste. It promotes a more sustainable approach by using materials efficiently and recycling them.
- Q: What are the benefits of 3D printing in the circular economy?
- A: 3D printing reduces transportation emissions, allows for local production, enables customization, and facilitates the repair and reuse of products, all of which contribute to a more circular and sustainable economy.
- Q: How does 3D printing help in closing the loop?
- A: 3D printing allows for the creation of new products from recycled materials, reducing the need for virgin resources. It enables the recycling and repurposing of waste materials, helping to close the loop in the production cycle.
- Q: What are the challenges of 3D printing in the circular economy?
- A: Some challenges include the limited availability of recycling infrastructure for 3D printed materials, the need for standardized recycling processes, and the potential environmental impact of certain 3D printing materials.
- Q: Can 3D printing be used for large-scale production?
- A: While 3D printing is commonly used for prototyping and small-scale production, advancements in technology are making it increasingly feasible for large-scale production. However, it may not always be the most efficient or cost-effective method for mass production.

Hello, I’m Archie Ewers, a dedicated Professional Print Application Consultant with a passion for 3D scanning solutions, educational 3D projects, engineering in 3D, and sustainability in 3D printing. With years of experience in the industry, I have developed a deep understanding of the intricacies and possibilities that this technology offers. Read More