
Why Periodontal Treatment is Crucial for Diabetic Patients
Introduction
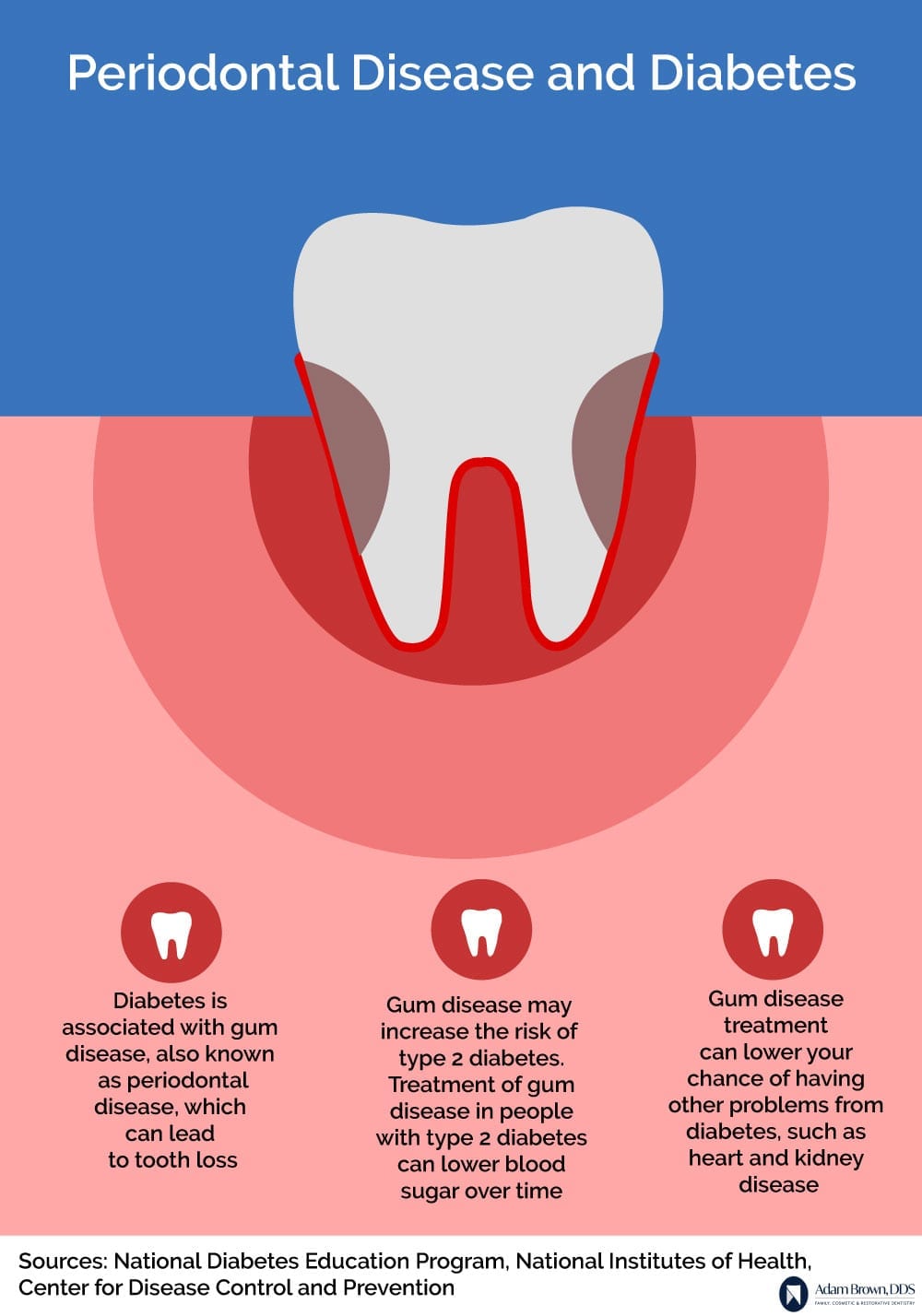
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It is characterized by high blood sugar levels and can lead to various complications if not properly managed. One such complication is periodontal disease, a serious gum infection that can have detrimental effects on oral health. This article explores the link between diabetes and periodontal disease, highlighting the importance of periodontal treatment for diabetic patients.
The Connection between Diabetes and Periodontal Disease
Research has shown a strong association between diabetes and periodontal disease. Diabetic individuals are more prone to developing gum infections due to their compromised immune system and reduced ability to fight off bacteria. Additionally, high blood sugar levels provide an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive, leading to the progression of periodontal disease.
Impact of Periodontal Disease on Diabetic Patients
Periodontal disease can have severe consequences for diabetic patients. It can worsen blood sugar control, making it more challenging to manage diabetes effectively. The inflammation caused by gum infections can increase insulin resistance, leading to higher blood sugar levels. This vicious cycle can further exacerbate the complications associated with diabetes.
Increased Risk of Complications
Diabetic individuals with untreated periodontal disease are at a higher risk of developing various complications. These include:
1. Cardiovascular Disease
Periodontal disease can contribute to the development of cardiovascular problems such as heart disease and stroke. The inflammation in the gums can spread to other parts of the body, including the blood vessels, increasing the risk of cardiovascular complications.
2. Kidney Disease
Diabetic patients already have an increased risk of kidney disease. When combined with periodontal disease, the risk becomes even higher. The inflammation and infection in the gums can affect the kidneys, leading to further deterioration of kidney function.
3. Eye Complications
Diabetes can cause various eye problems, including diabetic retinopathy and glaucoma. Periodontal disease can worsen these conditions by increasing inflammation and affecting blood flow to the eyes.
Summary
Diabetic patients are more prone to developing periodontal disease due to their compromised immune system and impaired ability to fight off infections. The relationship between diabetes and periodontal disease is bidirectional, meaning that not only does diabetes increase the risk of gum disease, but untreated gum disease can also worsen diabetes control. Research has shown that individuals with diabetes are more likely to experience severe gum disease, leading to tooth loss and other oral health complications.
Periodontal treatment plays a crucial role in managing diabetes and improving overall health outcomes. By addressing gum disease through professional cleanings, scaling and root planing, and other periodontal therapies, diabetic patients can reduce inflammation, control blood sugar levels, and enhance their overall well-being. Regular dental check-ups, proper oral hygiene practices, and collaboration between dental and medical professionals are essential for effective management of both diabetes and periodontal disease.
In conclusion, diabetic patients must prioritize periodontal treatment as part of their overall healthcare routine. By maintaining good oral health, individuals with diabetes can reduce the risk of complications, improve diabetes control, and enhance their quality of life. It is crucial for healthcare providers to educate diabetic patients about the importance of periodontal care and encourage regular dental visits to prevent and manage additional resources gum disease effectively.
- Q: Why is periodontal treatment crucial for diabetic patients?
- A: Periodontal treatment is crucial for diabetic patients because diabetes can increase the risk of developing gum disease. Gum disease, if left untreated, can lead to serious complications for diabetic individuals, including difficulty in controlling blood sugar levels and an increased risk of diabetic complications.
- Q: How does gum disease affect diabetic patients?
- A: Gum disease can affect diabetic patients by making it harder for them to control their blood sugar levels. Inflammation in the gums can cause insulin resistance, making it more challenging to manage diabetes effectively. Additionally, untreated gum disease can increase the risk of heart disease and other diabetic complications.
- Q: What are the benefits of periodontal treatment for diabetic patients?
- A: Periodontal treatment for diabetic patients can help improve gum health, reduce inflammation, and control gum disease. By managing gum disease, diabetic individuals may experience better blood sugar control, reduced risk of diabetic complications, and improved overall oral health.
- Q: What does periodontal treatment involve?
- A: Periodontal treatment typically involves professional dental cleaning, scaling and root planing, and in some cases, surgical interventions. These procedures aim to remove plaque, tartar, and bacteria from the gums, reduce inflammation, and promote gum tissue healing.
- Q: How often should diabetic patients undergo periodontal treatment?
- A: The frequency of periodontal treatment for diabetic patients may vary depending on the severity of gum disease and individual needs. It is best to consult with a dental professional who can assess the condition and recommend an appropriate treatment plan, which may include regular cleanings every three to four months.




